D QUAD – Moderate Pes Planus
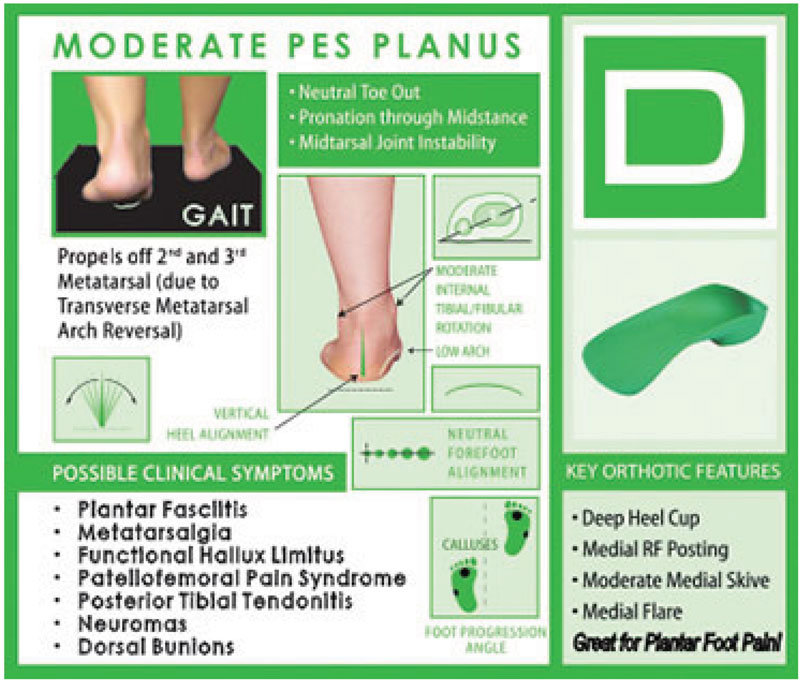
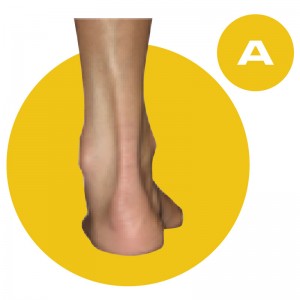
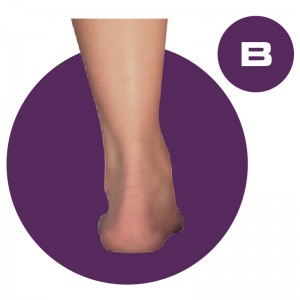
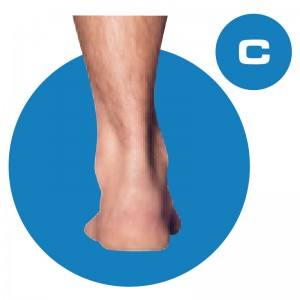
The D QUAD Foot-Type is a moderately over-pronated foot-type. This means that the foot rolls in too much and tends to be too flexible and loose, which makes for an unstable foundation. This foot typically has a fairly flat looking arch and someone with this foot type would be described as being ‘flat footed’, though several foot types have varying degrees of flat-footedness.
This foot-type is congenitally a partially unstable foot and is often diagnosed in children as developmental flat foot. Make no mistake, if you think that this child will “out-grow the deformity,” just ask Mom and Dad and their older siblings to take off their shoes and socks. If family members demonstrate similar foot characteristics, chances are that this child is not going to develop an arch.
If you want to know what it feels like to have the D QUAD Foot-Type, imagine walking barefoot in the sand at the beach for an extended time. Due to its unstable nature, all the bones in the feet tend to jiggle around too much and all the muscles and ligaments in the feet have to work double-time to try and hold everything in place in an attempt to stabilize the foot. People with this foot type tend to fatigue very easily and may not want to be very active, because their feet hurt. Common complaints for people with this foot type include: Forefoot pain, heel pain, knee pain and bunions.
We affectionately refer to people with this foot-type as the “Fred Flintstone walkers” because they tend to have a flat plodding type gait that is neither toe-in or toe-out.
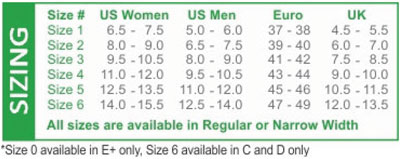
All Quadrastep Orthotics are available in Regular and Narrow Widths, and with a topcover an an additional charge.
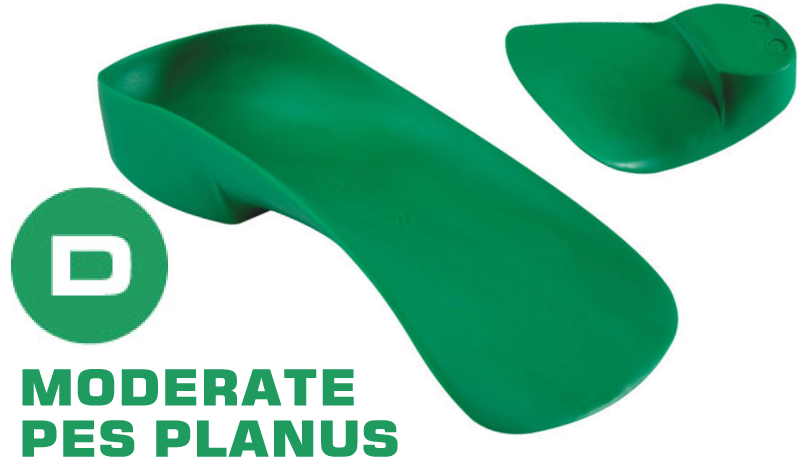

Key Orthotic Features:
- Deep Heel Cup
- Medial Rearfoot Posting
- Moderate Medial Skive
- Medial and Lateral Flare
D Quad Possible Clinical Symptoms
- Plantar Fasciitis
- Metatarsalgia
- Functional Hallux Limitus
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
- Posterior Tibial Tendonitis
- Neuromas
- Hallux Limitus